2.1 - Bonding, structure, and the properties of matter (Part 1)
Chemical bonds
- There are three types of strong chemical bonds: ionic, covalent and
metallic.
- In Ionic bonds, the positive and negative charges are attracted to each
other. It can only occur in compounds where metals are combined with non-metals.
- In Covalent bonds, the electrons are shared between the atoms. It happens
in most non-metallic elements and in most non-metal compounds.
- In Metallic bonds, the electrons are shared between the atoms, but the
atoms are held together by a network of metal ions. It occurs in metals.
Ionic bonds
- Ions are atoms that have a positive or negative charge formed by the
gain or loss of electrons.
- The loss or gain of electrons gives the ion a full outer shell of electrons.
- A full outer shell needs to have 8 electrons. Metals lose electrons, and
non-metals gain electrons.
- Since most of GCSE only focuses up to Calcium, for our purposes:
- Group 1 elements lose 1 electron
- Group 2 elements lose 2 electrons
- Group 3 elements lose 3 electrons
- Group 4 elements gain 4 electrons
- Group 5 elements gain 3 electrons
- Group 6 elements gain 2 electrons
- Group 7 elements gain 1 electron
- Group 8 elements do not gain or lose electrons
- Negative ions are called anions and form when atoms gain electrons, they have more electrons than protons.
- Positive ions are called cations and form when atoms lose electrons, they have more protons than electrons.
- Here's how it's represented (image stolen from spec):
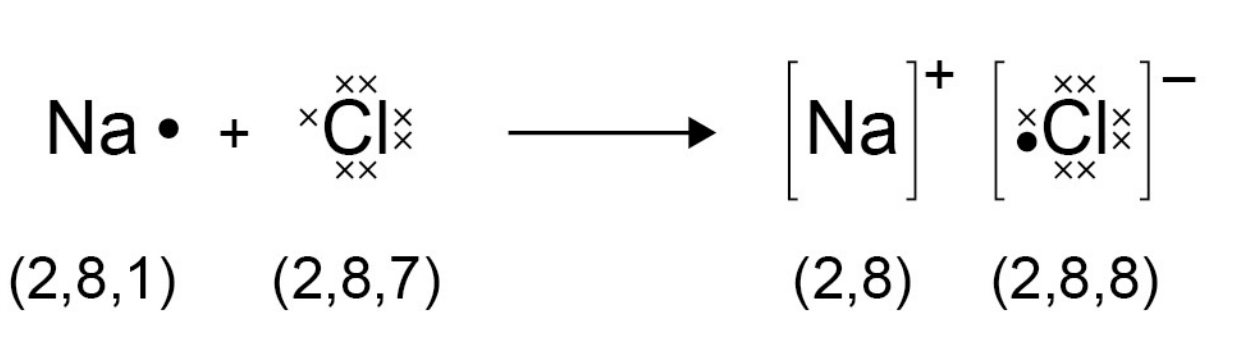
Ionic Structures
Giant Ionic Lattices
- This is a regular arrangement of alternating positive and negative ions.
- The ions are tightly packed together, and the electrons are evenly distributed.
- It is held together by the strong electrostatic forces of attraction between the ions, forming
the basis of ionic bonding.
- Due to the electrostatic forces, the lattice structures have high melting and boiling points.
- They allow regular shaped crystals to be formed.
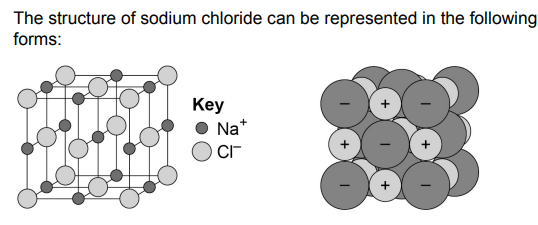 also stolen from the spec
also stolen from the spec
Ball-and-stick structure advantages/disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
